There are 4 different types of vaccines- Whole virion (Live attenuated and killed), Recombinant viral vector, Nucleic acid (mRNA/ DNA) and Protein based. Among them, I have listed 10 different brand names of vaccines which are developed for Covid-19 (Corona virus).
Here is a table for quick comparision and corelation among these vaccines developed for Covid-19.
Vaccine | Manufacturer | Storage | Dosage | Interval | Side effects |
KILLED or INACTIVATED VACCINES | |||||
Covaxin | Bharat Biotech, Hyderabad, India | 2-8℃ | 2 doses | 4-6 weeks | Site pain, fever |
Sinopharm | China National Pharmaceutical group, China | 2-8℃ | 2 doses | 3-4 weeks | Site pain, fatigue, diarrhoea |
Coronavac or Sinovac | Sinovac Biotech, China | 2-8℃ | 2 doses | 3 weeks | Site pain, fatigue, diarrhoea |
VIRAL VECTOR VACCINES | |||||
Covishield | Oxford University & AstraZeneca | 2-8℃ | 2 doses | 12-16 weeks | Site Pain, fever |
Sputnik V | Gamaleya National Centre, Russia | -18.5℃ (liquid form) 2-8℃ (dry form) | 2 doses | 3 months | Fatigue, headache, muscle pain |
Johnson & Johnson | Janssen Pharmaceutical company of Johnson & Johnson, USA | 2-8℃ | 1 dose | - | Tiredness, headache, muscle pain, fever, nausea |
m-RNA VACCINES | |||||
Pfizer | Pfizer Global Manufacturing (PGM), USA | -80 to -60℃ (6months) and 2-8℃ (up to 5 days) | 2-8℃ | 3-6 weeks | Pain at site, headache, tiredness, fever, chills |
Moderna | Moderna therapeutics, USA | -25℃ to -15℃ (6 months) and 2-8℃ (up to 5 days) | 2-8℃ | 28 -42days | Fever, chills, tiredness |
VIRAL PROTEIN-BASED VACCINES | |||||
Novavax NVX-CoV2373 | Novavax, Inc., USA [on Trial – Phase 3] | 2-8℃ | 2 doses | 12weeks | Site pain, tenderness, headache, fatigue |
Live Attenuated Vaccine | |||||
A50-18 vaccine (B-1strain) | Not Marketed yet. | 37℃ | 2 doses | 21 days | Not suitable for immunocompromised, Pregnant and lactating mother |
I. Whole virion vaccine:
There are two ways to utilize whole virion for vaccine preparation: a) Live attenuated b) Inactivated
1. Live attenuated vaccine:
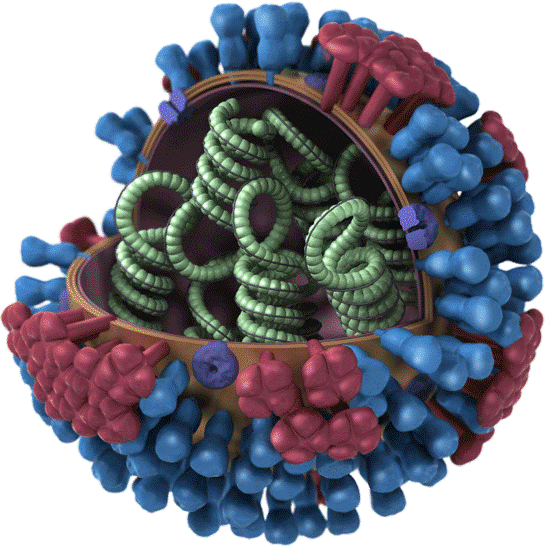
Live attenuated vaccines are those mutants or weakened form of the virus, which have ability to replicate and virtue of inability to cause any disease. That means they does not cause any illness in immunocompetent host related to that particular weakened virus.
Brand names of Live attenuated vaccines:
| A50-18 vaccine (B-1strain)- not yet marketed. It is still under study. |
Advantages of Live attenuated virus:
- They produce long lasting immunity involving B-cells and T-cells
- They are made up by well advanced technology but relatively simple to manufacture.
- They can retain all immunogenic components (major and minor)
- They are capable to induce mucosal immunity by stimulating IgA antibody production at local mucosal sites.
Disadvantages of Live attenuated vaccines:
- There is need of cautious cold storage (-70℃)
- They have a limited shelf life. So, viral stabilizer is added to their preparations.
- In immunocompromised individuals, they may cause disease.
- Interference by coinfection i.e., when you are infected with the same disease and you administer the live vaccine, it may inhibit replication of vaccine virus and thus, decreases its effectiveness.
- During the manufacturing process of live attenuated vaccine, adventitious contaminants or unrecognized agents may infect the culture substrate like- eggs, primary cell culture and hence allowing them to enter vaccine stock. Common contaminated viruses found in vaccines are- Avian leukosis virus, Simian polyomavirus SV40, Simian Cytomegalovirus.
2. Inactivated or killed vaccine:
Inactivated or killed virus is prepared by inactivating viruses with –
- Heat: Now a days, its unsatisfactory since it causes extensive denaturation of proteins.
- Chemical: They are inactivated by chemicals like- Phenol, Formalin, Betapropionolactone
- Ionising radiation: UV radiation (not used now a days, because of risk of multiplicity and reactivation). Gamma radiation.
Killed virus vaccines are prepared from whole virions generally stimulates the development of circulating antibodies against epitope of virus.
Brand names of Killed or Inactivated Covid-19 vaccines:
| Covaxin |
| Sinopharm |
| Coronavac or Sinovac |
Advantages of Inactivated vaccines:
- It is comparatively safer and stable. Since no live component used, so it is safer and can be given in patient with underlying comorbidities.
- The storage requirement of Killed vaccine is not demanding. It can be stored at normal refrigerator temperature i.e., 2-8℃.
- It can be given in combination with polyvalent vaccines
- These vaccines can be made when no acceptable attenuated vaccines are available.
Disadvantages of Inactivated vaccine:
- The cell mediated immunity response is generally poor by killed vaccines
- When it is given parenterally, it stimulates circulating antibodies (IgM and IgG) to satisfactory level. Sometimes, limited protection is seen because of local antibodies (IgA) is not induced adequately at natural port of entry or primary site of multiplication of virus infection, for example- nasopharynx for Covid virus.
- Some killed vaccine may induce hypersensitivity or allergic reaction to subsequent infection, owing to unbalanced immune response.
- Immunity Conferred is often brief or of short duration. So, booster dose is needed. But possible effect of repeated its administration, may manifest as hypersensitivity.
II. Recombinant Vector vaccine:
Vaccine antigen is produced by genetic engineering technologies.
Recombinant viral vector vaccine is prepared by utilizing live attenuated vaccine virus and adding it to genes encoding antigen present on newly emerging pathogen like Adenovirus, and termed as Vector. Hence these vaccines are named so.
The other vectors can be used in preparation of vector vaccines are: Vaccinia virus, Attenuated strains of polio virus, BCG strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, attenuated strains of Salmonella etc. So, vector virus here is genetically engineered for coronavirus protein formation.
There are 2 types of viral vector vaccines. They are:
- Replicating viral vector (which can replicate within the cells)
- Non-replicating viral vector (which cannot replicate within the cells)
Brand names of Recombinant viral vector vaccine for Covid-19:
| Covishield |
| Sputnik V |
| Johnson & Johnson |
Advantages of Viral vector vaccine:
- It can be stored at normal refrigerator temperature i.e.,2-8℃
- Based on advanced technologies.
- Vector virus is weakened virus and doesn’t produce disease in healthy immunocompetent individuals.
- It promotes strong immune responses involving B-cells and T-cells.
Disadvantages of viral vector vaccines:
- Relatively complex to manufacture
- If there is previous exposure to vector virus, it may hamper the effectiveness of the vaccine.
III. Nucleic acid vaccine:

Nucleic acid vaccine is based on genetic material and therefore, it can be DNA or RNA vaccine.
This nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) is inserted in the host cell to produce numerous copies of viral protein to produce an immune response.
Brand names of mRNA (Nucleic acid) vaccine for Covid-19:
| Pfizer/ BioNTech |
| Moderna |
Advantages of Nucleic acid vaccines:
- Relatively easy to manufacture.
- It is less costly.
- There is strong immune response because the antigens are produced in large quantities, inside the host cells.
Disadvantages of Nucleic acid vaccines:
- RNA vaccines are stored in ultra-cold storage with temperature -70℃ or even lower. So, countries which can afford specialized ultra-cold storage are very less.
IV. Protein Subunit vaccine
Protein based vaccine uses viral protein or its fragment or shells to produce an immune response.
There are 2 types of protein-based vaccines which is being developed for coronavirus infection. These are:
- Protein Subunit vaccine or Nanoparticle Vaccine – Prefusion spike protein (glycoprotein) which mediates host cell entry. An introduction of proline amino acid to S2 subunit and stabilise the protein in a prefusion conformation. It allows the induction of potent neutralising antibodies, experiment done in mice.
- Virus like particle vaccine
Brand names of Protein based vaccine for Covid-19:
| Novavax NVX-CoV2373 – under Phase 3 trial |
Advantages of Protein Based vaccines:
- Since there is only part or fragments of protein used in vaccine preparation, there is very fewer side effects
Disadvantages of Protein Based vaccines:
- Immune response produced by protein-based vaccine is very weak. Therefore, they require adjuvants, to boost up the immune response.